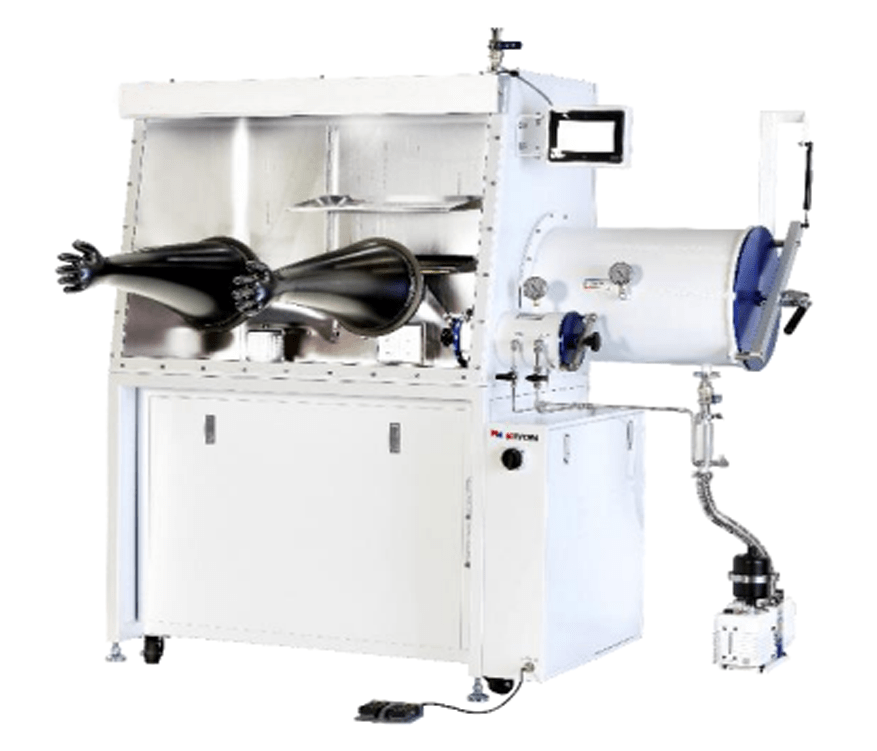
Model: 011AS (2 Port)
What is a Glovebox?
A glovebox, is a piece of equipment used in chemical laboratories and industrial facilities to handle materials sensitive to humidity, oxidation or airborne contamination. This device makes it possible to work with substances in an inert atmosphere, that is to say in the absence of oxygen, nitrogen or other reactive gases.
Construction and Operation of gloveboxes
The glovebox is a sealed, cube-shaped chamber, usually made of stainless steel or chemical-resistant plastic. It is equipped with two or more rubber gloves attached to airtight cuffs, which allow the operator to handle the samples inside the box without letting in air or moisture.
A glovebox is often connected to a pumping system to maintain a continuous inert atmosphere, by circulating an inert gas, such as nitrogen, argon or helium through special filters.
Key Features and Components gloveboxes
Gloves used in gloveboxes are usually made of nitrile or latex and can be replaced easily when needed, as they can degrade over time or become contaminated with chemicals or microorganisms.
Some glovebox models are equipped with a HEPA filtration system to remove fine particles and contaminants from the air in the box, thus ensuring better safety for operators.
Common Applications of gloveboxes
Common applications of gloveboxes include the handling of explosive materials, the analysis of air or moisture sensitive materials, the synthesis of specific materials, and the study of toxic or radioactive chemicals.
They are a safe and reliable solution for working with sensitive materials, providing an inert atmosphere to prevent unwanted reactions and contaminations, while providing overall protection for operators.


